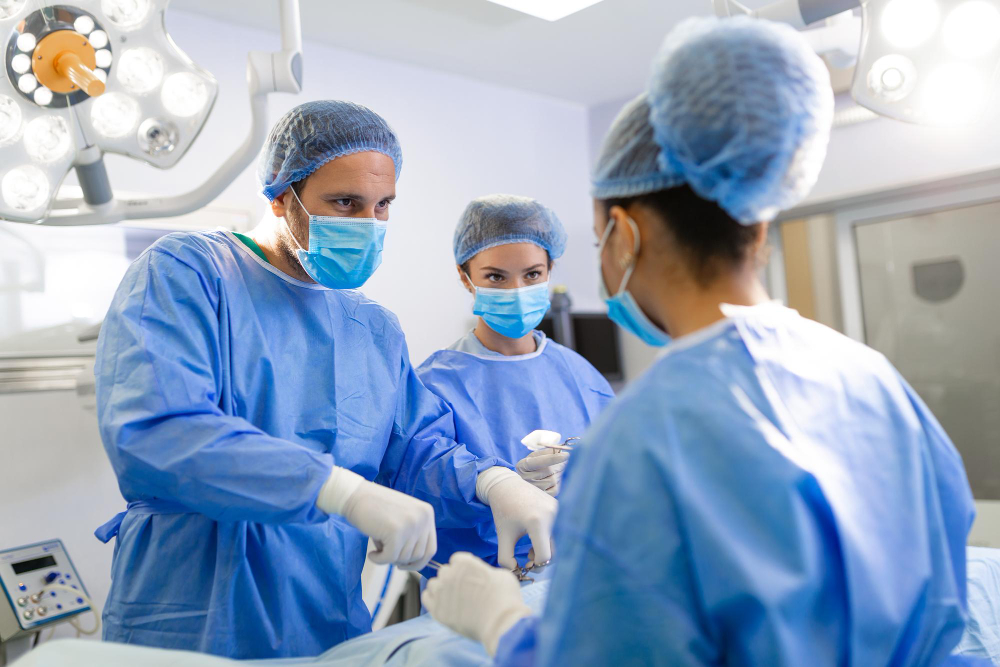
The rapid expansion of the range of surgical procedures that can be done using minimally invasive surgical (MIS) techniques has raised a lot of questions about who will benefit from these types of procedures and what surgeries it is best suited for. As usual with such situations, myths abound that cause confusion and uncertainty in the minds of patients. In this article, we will try to dispel the most common myths so that those contemplating surgery have a more accurate understanding of the options available to them. Before going any further, it must be emphasized that while a patient has a say in the type of procedure he or she will undergo, the final decision must be left to the surgeon because there are always complex medical considerations that the patient will not be aware of and which require specialized medical knowledge to appreciate.
The Myths
-
MIS is only for simple minor surgeries.
Fact: While MIS was initially used for minor procedures, it has now evolved into a technique that can be used for even the most complex of surgeries. It is now commonly used for organ removal, cardiac surgery, cancer treatments and more. MIS is also routinely used for orthopedic, gynecology, urology and other complex procedures. The range of MIS options keeps increasing.
-
It is a new technique and is experimental in nature.
Fact: MIS has been in use for over 30 years. During this time, it has proven itself to be a stable, reliable and effective technique. It is now commonly used for various types of surgeries across the globe and there is no evidence of it being in any way inferior or less effective than traditional surgery.
-
MIS results are not as good as traditional surgery results.
Fact: The decision to opt for MIS is taken only where there is absolute certainty that the results will be as good as that with traditional surgery. In fact, one of the key benefits of MIS is that the post-surgical pain and discomfort is less, resulting in less medication being used after surgery.
-
Recovery time is the same for MIS and traditional surgery.
Fact: Because MIS involves smaller incisions, there is less surgical trauma and blood loss as compared to traditional surgery. There is also less pain and a lower risk of infection. These factors all contribute to a faster recovery as compared to traditional surgery.
-
MIS is riskier than traditional surgery.
Fact: MIS is performed by surgeons who have been trained in minimally invasive surgical techniques. It is only used when it does not involve any additional surgical risk. The smaller incisions and lower blood loss, coupled with the reduced risk of infection, offer significant benefits to patients.
-
If robotic surgery is being used, the patient is at the mercy of machines.
Fact: Robotic surgery is an advanced form of MIS. It does not mean that the surgery is performed by a machine or robot. In robotic surgery, high-precision robotic tools and instruments are used to perform the surgery, but these are controlled by a surgeon throughout the procedure. Robotic surgery gives the surgeon access to high-precision instruments that serve to increase his skill level.
-
MIS is not suitable for elderly patients.
Fact: In many cases, MIS offers significant benefits for elderly patients, especially those who have other health conditions that complicate treatment. The lower levels of physical and psychological stress associated with MIS, including shorter recovery periods, mean that elderly patients can leave the hospital sooner and return to the environments in which they feel comfortable.
-
MIS cannot be used if a patient has had previous traditional surgery.
Fact: If a person has had prior traditional surgeries, it does not mean that MIS is automatically ruled out. The surgeon will study the patient’s overall health, the effects of the previous surgery and other health parameters to assess the viability and benefits of performing MIS.
-
MIS is more expensive than traditional surgery.
Fact: This myth stems from the early days of MIS when the new technology and equipment required raised costs. Today, the impact of the use of MIS technology has greatly reduced cost. In fact, in some cases, the overall cost of MIS to a patient may be less than that with traditional surgery because of the shorter hospital stay and the more rapid return to normal life and activities.
-
MIS is recommended based on the preferences of the surgeon or hospital.
Fact: No reputable surgeon or hospital will ever do this. The decision on which type of surgery to perform is based purely on an evaluation of what is in the best interest of the patient and the expected results of the procedure. Personal biases do not enter the picture.
If you have a medical condition that requires surgery, it is vital that you have the procedure done at a hospital that has world-class surgeons, and the latest and most advanced surgical procedures and treatment technology. A multispecialty hospital like New Medical Centre (NMC) in Pondicherry is a prime example of such a hospital. Not only are the best doctors and surgeons to be found here, but the range of medical specializations available is a huge benefit for patients because disorders can affect more than one part of the body. Moreover, the availability of other specialties also means there will be no delays that could adversely impact a patient’s recovery. Patients at NMC have both traditional as well as MIS surgical options available to them. Doctors and surgeons explain the benefits of each type of procedure and recommend a specific course of action based on the needs of the individual patient.
Why choose minimally invasive surgeries over open surgeries?
Frequently Asked Questions About Minimally Invasive Surgery
- What is minimally invasive surgery (MIS)?
Minimally invasive surgery (MIS) is a surgical technique that uses small incisions and specialized instruments, including laparoscopic or robotic tools, to perform procedures with minimal damage to surrounding tissues compared to traditional open surgery. - Is minimally invasive surgery only used for minor procedures?
No. While MIS was initially used for simpler surgeries, it is now widely used for complex procedures such as organ removal, cancer surgery, cardiac surgery, orthopedic, gynecological, and urological operations. - Is minimally invasive surgery a new or experimental technique?
No. MIS has been in practice for over 30 years and is a well-established, reliable, and globally accepted surgical approach with proven outcomes. - Are the results of MIS as effective as traditional surgery?
Yes. MIS is chosen only when surgeons are confident that outcomes will be equal to or better than traditional surgery. In many cases, MIS also results in less pain, reduced complications, and faster recovery. - Does minimally invasive surgery reduce recovery time?
Yes. Because MIS involves smaller incisions, patients experience less surgical trauma, reduced blood loss, lower infection risk, and faster healing compared to traditional open surgery. - Is minimally invasive surgery riskier than open surgery?
No. MIS is performed only when it does not increase surgical risk. In fact, smaller incisions and reduced blood loss often make MIS safer for suitable patients.