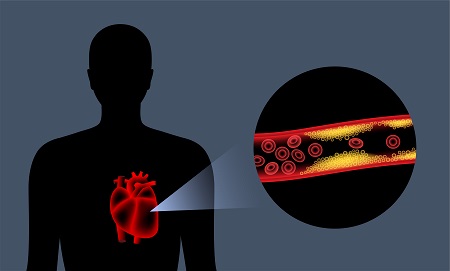
The coronary arteries supply blood to the heart. Coronary Artery disease (CAD) happens because over time a waxy substance known as plaque (a combination of fat, cholesterol and other substances) builds up in the arteries, constricting them and reducing the blood flow. The build-up happens very slowly but in the end, it will reduce blood flow so much that heart failure, a heart attack or arrhythmia occurs. The plaque can also break away from the artery wall. Blood cells will collect to try to repair the damage and will form clots that will stop or severely restrict blood flow and may cause a heart attack.
Types Of Coronary Artery Disease
There are 2 main forms of CAD:
- Stable Ischemic Heart Disease: This is a chronic condition that develops slowly over the years, gradually reducing oxygen rich blood supply to the heart. Patients may feel some symptoms but in most cases, they are able to live with them by taking precautions.
- Acute Coronary Syndrome: This is an emergency situation that occurs when plaque breaks away in the artery and the resulting blood clot blocks blood flow to the heart causing a heart attack.
Symptoms Of Coronary Artery Disease
Because plaque buildup occurs so slowly, the symptoms may not appear for years and when they do, they may be mild. These are the common signs that a person may be suffering from CAD:
- Stable Angina: This is the most common symptom and is a temporary pain or discomfort in the chest. It comes and goes in a predictable manner. For example, it will occur during heighten physical activity or emotional distress. It fades away with rest or medication.
- Shortness Of Breath: Physical activity can cause shortness of breath.
In some cases, the first indication of CAD is a heart attack. The signs of common signs of this are:
- Mild or severe angina that may take the form of pain, heaviness, tightness, burning, numbness, or a dull ache in the chest that may spread to the shoulders, arms, neck, back or jaw.
- Breathlessness and difficulty in breathing.
- Feeling lightheaded and/or dizzy.
- Heart palpitations.
- Severe fatigue.
- Nausea, vomiting and other feelings of gastric discomfort. These are often mistaken for indigestion.
- Severe weakness.
Women may feel additional symptoms including:
- Sudden onset of insomnia.
- Feeling that the heart is racing.
- Hot flashes.
Causes Of Coronary Heart Disease
Atherosclerosis is the build-up of plaque in the arteries throughout the body. When the build-up in the coronary arteries restricts blood flow, it is CAD. Plaque build-up occurs with time as the body ages. Within limits, it is not a health risk. However, when the plaque becomes so great it affects the flow of blood to the heart, it becomes a very serious medical concern. Among the main causes of plaque build-up are:
- Genetic factors such as a family history of high cholesterol.
- High blood pressure
- Being overweight
- Diseases like diabetes and metabolic syndrome.
- Smoking.
- Excessive alcohol consumption.
- Lack of adequate exercise.
- An unhealthy diet.
- Stress, depression and anger.
Also Read: Yoga And Stress Relief
Diagnosing Coronary Artery Disease
To diagnose CAD a cardiologist will:
- Study the patient’s personal and family medical history.
- Use an electrocardiogram to measure the heart’s electrical activity and assess heart damage.
- Stress tests of various types to assess the heart’s function when the body is active.
- Use an echocardiogram that uses sound waves to evaluate your heart’s structure and function.
- Chest x-rays to see the heart and look for signs of damage.
- Do a coronary calcium scan to measure the amount of calcium present in the arteries.
- Use a Computed Tomography (CT) coronary angiogram to view a 3D image of the heart as it beats.
- Use blood tests to measure the levels of blood sugar, triglycerides, cholesterol, etc.
- Use cardiac catheterization which is inserting a thin flexible tube into a blood vessel in the arm or leg and manipulating it up to the heart. Once there a dye will be injected into the heart through the catheter so that a detailed x-ray image of the inside of the heart may be obtained.
Also Read: Common Tests To Diagnose Heart Disease
Treatment For Coronary Artery Disease
A multipronged approach is required to treat CAD. The first step is lifestyle modification which includes:
- Dietary changes to control the intake of fats, sodium sugar and other substances that contribute to the development of plaque.
- Stopping smoking and recreational drug use or substance misuse.
- Regular exercise.
- Weight control.
- Stress management.
If lifestyle changes are not enough, the doctor may prescribe medication to increase heart health. These may include blood thinners, anti-clotting medication, beta-blockers, nitroglycerin, ACE inhibitors, statins, immunosuppressants, etc.
If the lifestyle changes and medication do not produce the required results, surgery may be advised. The most common of these procedures are:
- Angioplasty: A thin flexible tube with a deflated balloon at the tip is inserted into a blood vessel and moved up to the blocked artery. The balloon is then carefully inflated which stretches the artery to allow for more blood to flow. In some cases, a stent (a tiny tube) is inserted into the stretched part of the artery to keep it open.
- Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting: In this procedure blood vessels are taken from other parts of the body and used to create a detour around the blocked artery. The blood flow through the grafted blood vessel will be unobstructed.
Prevent Coronary Artery Disease
There are several things that everyone (not just those at high risk of CAD) should do to protect the heart. These include:
- Regular health checkups at a hospital that has a programme of health checks to suit people of all age groups. These will provide early warning of any incipient heart conditions so that early treatment may begin.
- Keeping to a healthy weight.
- Avoiding tobacco use of all kinds.
- Limiting alcohol consumption.
- Exercising regularly.
- Having a healthy diet.
- Managing stress levels through yoga or other relaxation techniques.
Coronary Artery disease is a serious matter. If you suspect you may have it, do not delay diagnosis and treatment. If you are a patient of CAD, treatment at a hospital with a specialized cardiology department will ensure that you get the best treatment. If you have no symptoms of CAD, it is still wise to have regular checkups at a hospital that has a range of health checkup options to suit all health concerns and age groups. Early detection makes treatment much easier.